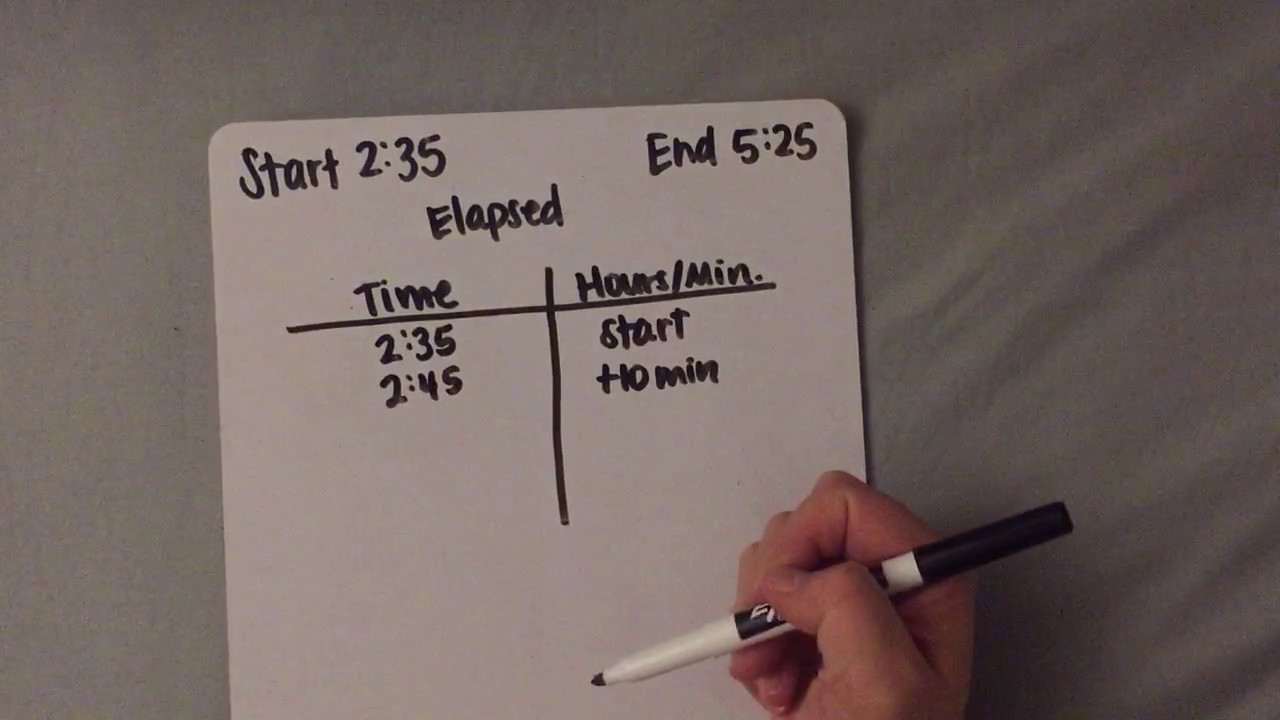
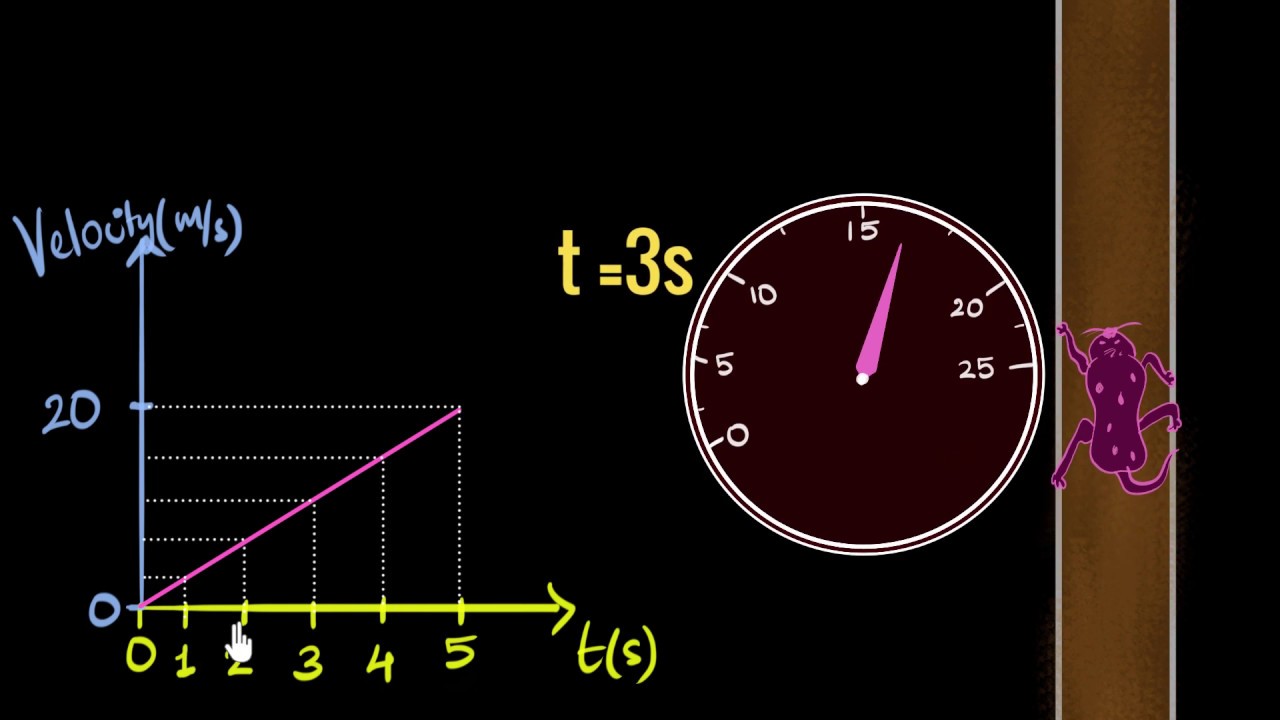
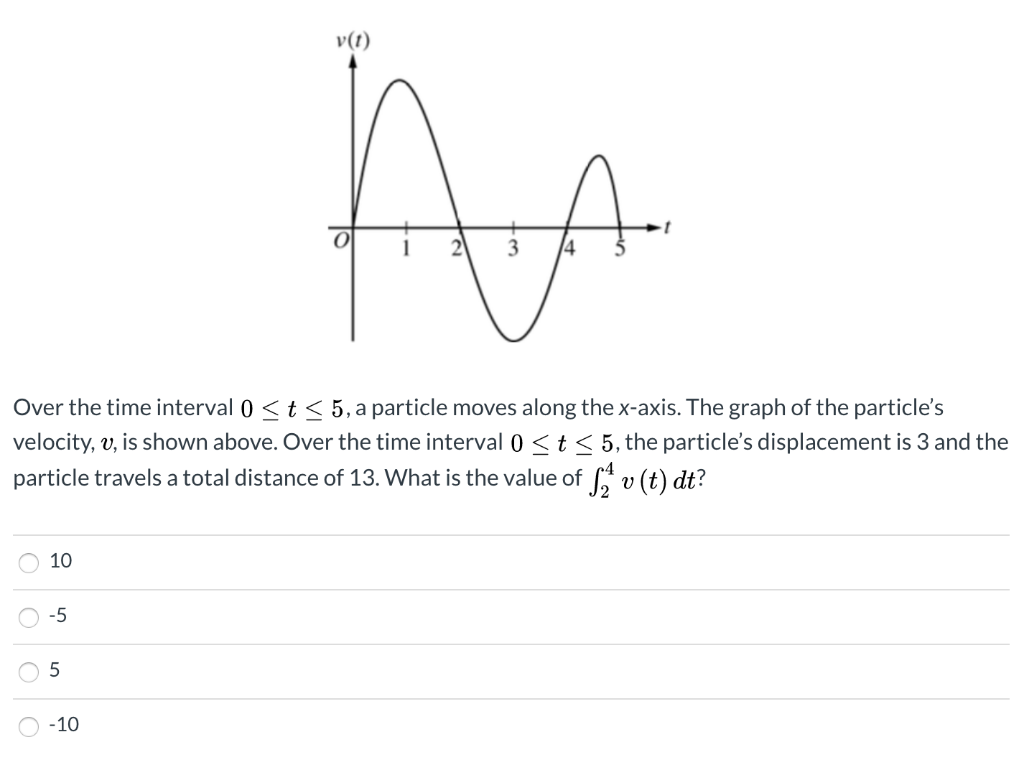
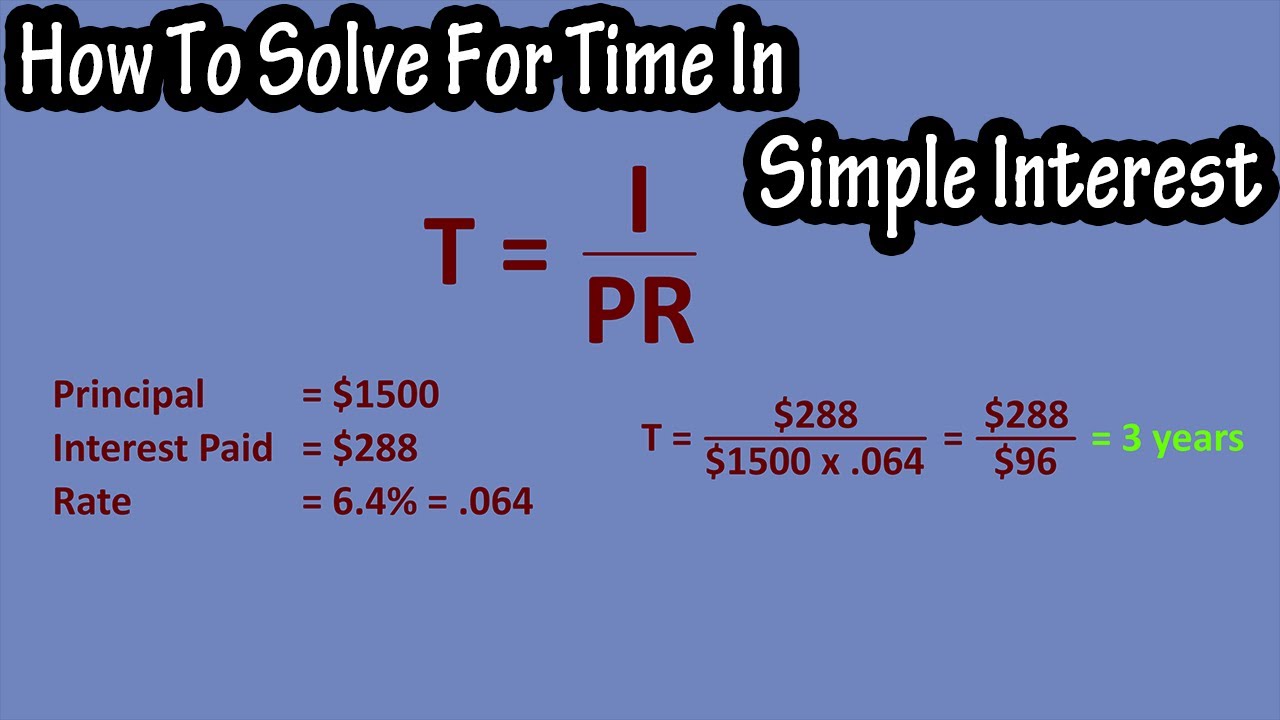
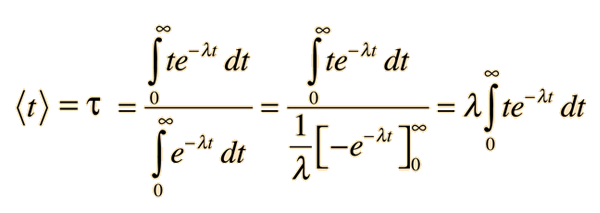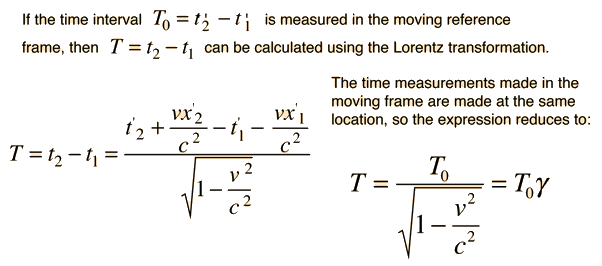The relation between the time t and position x for a particle moving on x axis is given by t = px² + qx, where p and q are cons†an ts. The
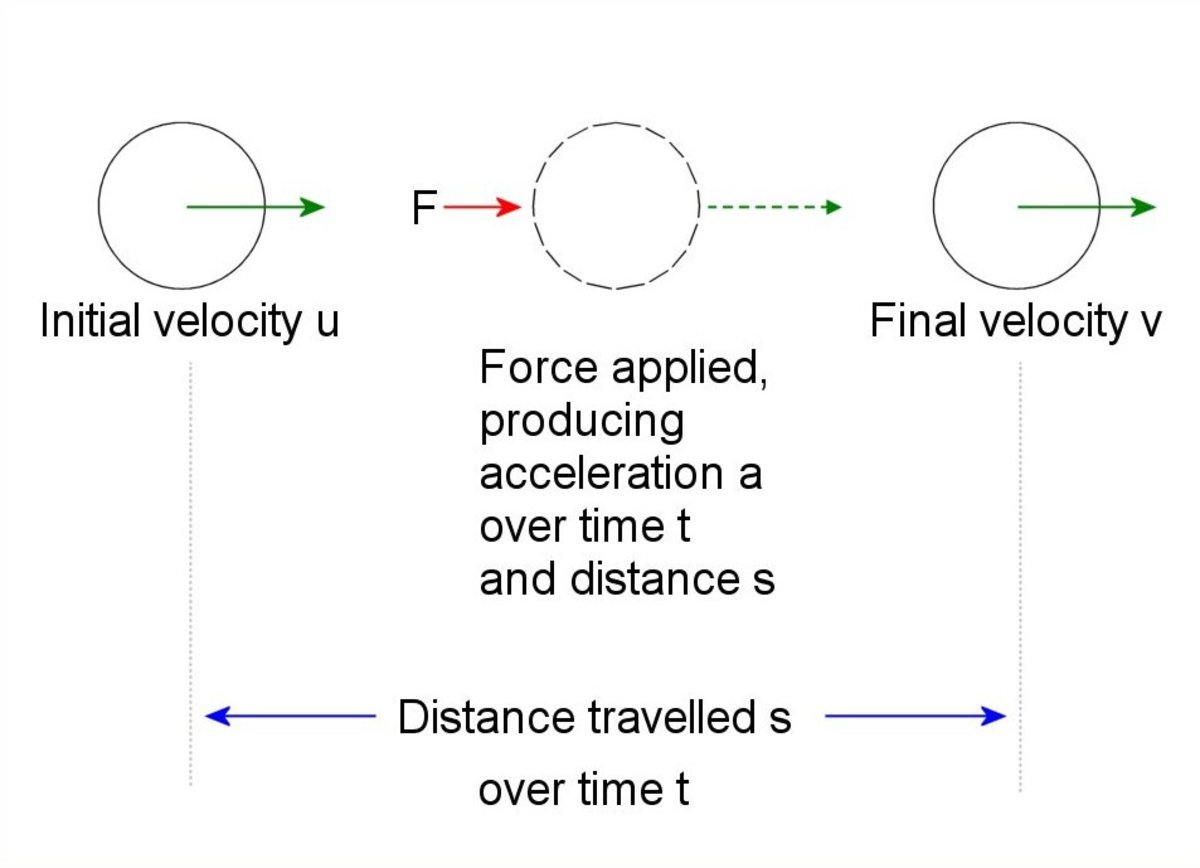
How to Solve Projectile Motion Problems: Applying Newton's Equations of Motion to Ballistics - Owlcation

The relation between time t and distance x is t = ax^2 + bx where a and b are constants.The acceleration is